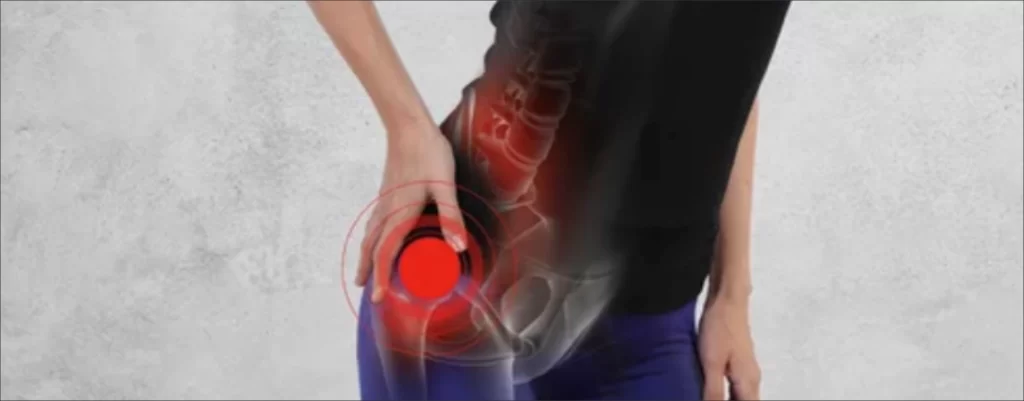
HIP PAIN: AN OVERVIEW
Hip pain is a common issue that affects individuals of all ages, from teenagers to the elderly. The hip is a ball-and-socket joint that connects the thigh bone to the pelvic bone and plays an important role in movements such as walking, running, and jumping. The hip is also involved in maintaining stability and balance, making it a crucial part of the body. When the hip joint experiences pain or discomfort, it can cause significant disruptions to daily activities.
ANATOMY OF THE HIP
The hip joint is formed by the interaction between the head of the femur (thigh bone) and the acetabulum (socket) of the pelvic bone. The joint is cushioned by a layer of cartilage, known as articular cartilage, which helps to absorb shock and reduce friction between the bones. The joint is also surrounded by a capsule made up of strong ligaments that help to stabilize it. In addition to these structures, the hip also contains several muscles, tendons, and bursae (small fluid-filled sacs) that work together to ensure smooth movement and stability.
BIOMECHANICS OF THE HIP
The hip is involved in a wide range of movements and is able to bear significant weight and force due to its strong anatomy and the support provided by surrounding muscles and ligaments. The hip joint has a large range of motion, allowing for movements such as flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. The biomechanics of the hip are complex and involve the coordinated movement of multiple structures.
CAUSES OF HIP PAIN
There are many factors that can contribute to hip pain, including:
· Arthritis: Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can cause the cartilage in the hip joint to wear down, leading to pain and stiffness.
· Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae surrounding the hip joint can cause pain and discomfort.
· Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons surrounding the hip joint can cause pain and discomfort.
· Fractures: A fracture in the hip can cause pain and instability.
· Muscle strains: Overuse or injury to the muscles surrounding the hip can cause pain.
· Referred pain: Hip pain can sometimes be referred from other areas of the body, such as the back or knee.
PREVENTION TIPS FOR HIP PAIN
· Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight places additional stress on the hip joint and can contribute to the development of hip pain.
· Engage in regular physical activity: Staying active helps to maintain the strength and flexibility of the hip joint.
· Warm up before physical activity: Warming up helps to reduce the risk of injury and improve performance.
· Use proper technique: Using proper technique when participating in physical activity helps to reduce the risk of injury and improve performance.
· Wear appropriate footwear: Wearing shoes with good support and cushioning can help to reduce the risk of injury and protect the hip joint.
TREATMENT FOR HIP PAIN
There are many treatment options available for individuals experiencing hip pain, including physiotherapy, manual therapy, and various forms of electotherapy modalities. Here are some of the most common treatment options:
Physiotherapy and manual therapy: Physiotherapists use a variety of manual therapy techniques to help alleviate hip pain, including soft tissue , joint mobilization, and stretching.
Myofascial releases: This technique involves the manual release of tight or restrictive fascia, which can help to reduce pain and improve range of motion.
Muscle energy technique: This technique involves the use of active contraction and release of muscles to improve joint mobility and reduce pain.
Proprioceptive exercises: Proprioceptive exercises are designed to improve the body’s awareness of its position in space, and can help to improve stability and reduce the risk of injury.
Strengthening exercises: Strengthening exercises are designed to improve the strength and stability of the hip joint, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall function.
Laser therapy: Laser therapy is a non-invasive form of treatment that uses low-level laser light to reduce pain and promote healing.
Electotherapy modalities: Electotherapy modalities, such as TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation), use electrical stimulation to reduce pain and improve function.
In conclusion, hip pain can be caused by a range of factors, including arthritis, bursitis, tendinitis, fractures, muscle strains, and referred pain. Treatment options include physiotherapy, manual therapy, myofascial releases, muscle energy technique, proprioceptive exercises, strengthening exercises, laser therapy, and electotherapy modalities. By seeking proper treatment and following prevention tips, individuals can reduce the risk of hip pain and maintain healthy, functional hips.