THE IMPORTANCE OF PROPER POSTURE AND ALIGNMENT AND HOW PHYSIOTHERAPIST CAN HELP
Posture and alignment are fundamental aspects of human body mechanics that significantly impact our overall health and well-being. Maintaining good posture and alignment is crucial for preventing musculoskeletal disorders, reducing the risk of injury, and promoting optimal bodily functions. In this response, we will delve into the concept of posture, alignment, their importance, and tips for achieving and maintaining proper posture and alignment.

Posture can be defined as the position in which we hold our bodies while standing, sitting, or lying down. It is the result of the interaction between various body parts, including the spine, muscles, joints, and ligaments. Posture is influenced by several factors, such as genetics, habits, occupational activities, and lifestyle choices.
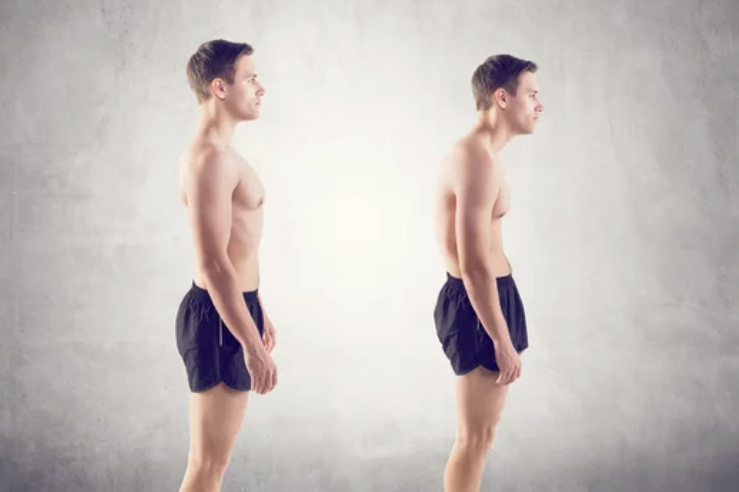
Good posture is characterized by a neutral alignment of the spine, which means that the natural curves of the spine are maintained in a balanced and aligned position. The spine has three primary curves: the inward curve of the neck (cervical curve), the outward curve of the upper back (thoracic curve), and the inward curve of the lower back (lumbar curve). When these curves are properly aligned, they distribute forces evenly throughout the body, reducing stress on the muscles, joints, and ligaments.
Proper alignment, on the other hand, refers to the correct positioning of the bones and joints in relation to each other. It ensures that the body’s structural components are stacked in a way that promotes optimal function and minimizes strain on the supporting structures.
Maintaining good posture and alignment is crucial for several reasons, poor posture and alignment can lead to various musculoskeletal issues, including back pain, neck pain, headaches, and joint problems. When the body is misaligned, certain muscles become overworked, while others become weak and inactive, leading to muscle imbalances. These imbalances can cause chronic pain and increase the risk of injury. Spine is a crucial component of our musculoskeletal system, protecting the spinal cord and supporting the body’s weight.
Proper posture and alignment help maintain the spine’s natural curves and reduce the risk of spinal disorders, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and degenerative disc disease. Good posture allows the lungs to fully expand and contract, facilitating optimal breathing.
Proper alignment also ensures that the organs have enough space and can function efficiently. Slouched posture, on the other hand, can compress the chest cavity and restrict lung capacity.
Maintaining proper posture and alignment can improve energy levels and overall mood. Good posture allows for efficient movement and reduces muscle fatigue. It can also enhance body awareness and self-confidence.
THE EFFECTS OF POOR POSTURE AND ALIGNMENT ON OUR HEALTH:
Posture and alignment play a crucial role in maintaining musculoskeletal health, preventing injuries, and promoting overall well-being. By being mindful of our posture, adopting ergonomic practices, strengthening our core and back muscles, and making conscious lifestyle choices, we can achieve and maintain proper posture and alignment. It is a continuous process that requires self-awareness and consistent effort, but the benefits are well worth it in the long run.

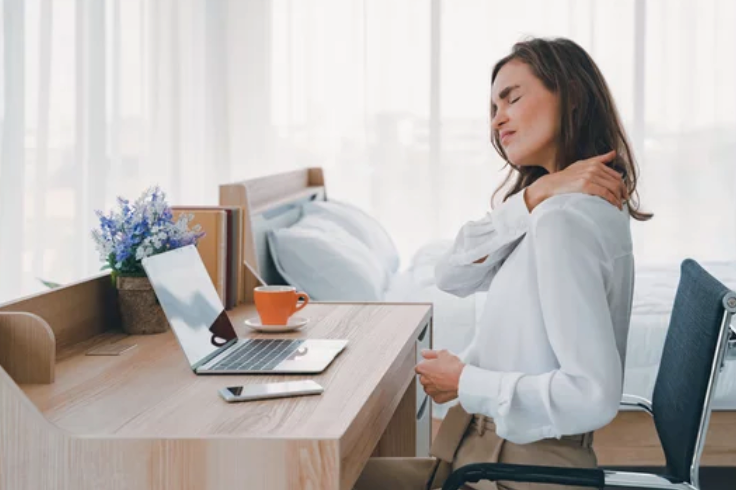
Poor posture and alignment can have significant effects on our overall health and well-being. When our bodies are not properly aligned, it can lead to a variety of musculoskeletal problems and other health issues. In this response, we will explore in detail the effects of poor posture and alignment on our health.
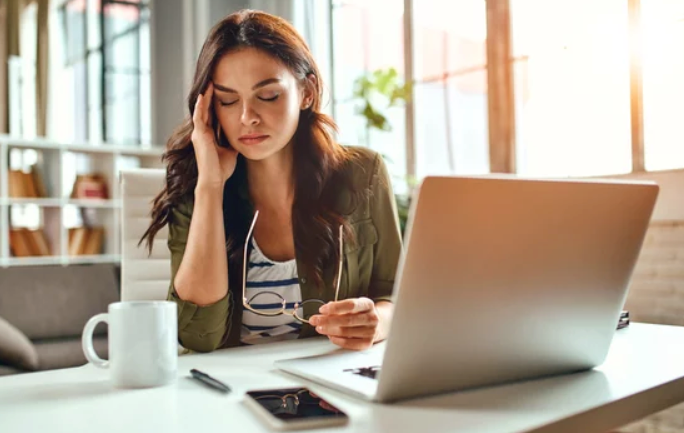

- MUSCULOSKELETAL PAIN: One of the most common effects of poor posture and alignment is musculoskeletal pain. When we slouch or hunch over, it puts excessive strain on our muscles, ligaments, and joints. Over time, this can lead to muscle imbalances, tension, and discomfort. The most commonly affected areas include the neck, shoulders, upper back, and lower back. Chronic poor posture can contribute to conditions such as neck pain, shoulder impingement, thoracic outlet syndrome, and lower back pain. The misalignment of the spine and joints can also increase the risk of developing degenerative conditions like arthritis.
- HEADACHES: Poor posture can contribute to tension headaches and migraines. When we have forward head posture or rounded shoulders, it can cause increased tension in the neck and shoulder muscles. This tension can lead to referred pain in the head and result in frequent headaches. Additionally, poor alignment can affect blood flow to the head and neck, further exacerbating headache symptoms.
- DIGESTIVE ISSUES: Posture and alignment can also impact our digestive system. Slouching or sitting in a hunched position compresses the abdominal organs, including the stomach and intestines. This compression can interfere with proper digestion and lead to issues such as acid reflux, bloating, and constipation. Good posture allows the abdominal organs to have sufficient space for optimal function and digestion.
- BREATHING PROBLEMS: Poor posture can affect our breathing patterns and lung capacity. When we have rounded shoulders and a hunched back, it restricts the expansion of the chest cavity. This can make it harder to take deep breaths and can contribute to shallow breathing. Inefficient breathing patterns can lead to decreased oxygen intake, reduced lung function, and an increased risk of respiratory infections. Good posture allows for proper expansion of the chest, allowing the lungs to function optimally.
- POOR CIRCULATION: Misaligned posture can also impede proper circulation throughout the body. When we slouch or sit in a compressed position, it can restrict blood flow and create areas of congestion. Poor circulation can lead to symptoms such as cold hands and feet, swelling in the legs and ankles, and increased risk of blood clots. Good posture promotes healthy blood flow, ensuring that oxygen and nutrients are effectively delivered to the body’s tissues.
- FATIGUE AND ENERGY LEVELS: Maintaining poor posture requires our muscles to work harder to support the body. Over time, this can lead to muscle fatigue and a feeling of constant tiredness. Additionally, poor posture can contribute to inefficient movement patterns, leading to decreased energy levels and reduced overall physical performance.
- MOOD AND CONFIDENCE: Our posture also has an impact on our mental and emotional well-being. Numerous studies have shown a connection between posture and mood. Slouched or hunched postures are associated with lower self-esteem, decreased confidence, and negative emotions. On the other hand, upright and open postures are linked to increased self-confidence, improved mood, and a positive mindset.
- SPINAL HEALTH: Poor posture and alignment can have long-term effects on the health of our spine. When we consistently maintain positions that place stress on the spine, it can contribute to spinal misalignment, increased wear and tear on the spinal discs, and the development of degenerative conditions such as herniated discs and spinal stenosis. These conditions can cause chronic pain, limited mobility, and potentially require medical intervention.
It is important to note that poor posture and alignment are often the result of habitual behaviors and lifestyle choices. Factors such as sedentary lifestyles, prolonged sitting, improper ergonomics, weak core muscles, and lack of body awareness can contribute to poor posture. The good news is that with awareness and conscious effort, we can improve our posture and alignment and mitigate the negative effects on our health.
HOW PHYSIOTHERAPISTS CAN HELP IMPROVE POSTURE AND ALIGNMENT:
Physiotherapists play a crucial role in helping individuals improve their posture and alignment. As experts in assessing and treating musculoskeletal conditions, they possess the knowledge and skills to identify postural issues and develop personalized treatment plans. Through a combination of manual therapy, exercise prescription, and education, physiotherapists can help individuals achieve optimal posture and alignment. In this response, we will explore in detail how physiotherapists can assist in improving posture and alignment.
- COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT: Physiotherapists begin by conducting a thorough assessment of an individual’s posture and alignment. This may involve observing the individual’s standing, sitting, and walking posture, assessing the alignment of the spine, pelvis, and limbs, and identifying any muscle imbalances or asymmetries. The assessment may also include analyzing movement patterns and identifying any factors contributing to poor posture or alignment.
- MANUAL THERAPY: Physiotherapists often utilize manual therapy techniques to address musculoskeletal imbalances and restore proper alignment. These techniques may include joint mobilizations, soft tissue release, myofascial release, and trigger point therapy. Manual therapy helps release tight muscles, improve joint mobility, and reduce pain, thereby allowing for better alignment and posture.
- EXERCISE PRESCRIPTION: Physiotherapists prescribe specific exercises and stretches to target weak muscles, strengthen core muscles, and improve flexibility. These exercises are tailored to address the individual’s unique postural imbalances. For example, if an individual has forward head posture, exercises to strengthen the deep neck flexor muscles and stretch the chest and upper back may be recommended. Physiotherapists also provide guidance on proper form and technique to ensure exercises are performed correctly and effectively.
- CORE STABILIZATION: A strong core is essential for maintaining good posture and alignment. Physiotherapists often incorporate core stabilization exercises into their treatment plans. These exercises target the deep abdominal muscles, back extensors, and pelvic floor muscles to improve core strength and stability. By strengthening the core, individuals can better support their spine and maintain proper alignment.
- POSTURAL RETRAINING: Physiotherapists educate individuals about proper posture and provide postural retraining techniques. They teach individuals how to align their spine, pelvis, and limbs correctly in different positions, such as sitting, standing, and walking. Physiotherapists may use mirrors or video analysis to provide visual feedback, allowing individuals to better understand and correct their posture. They also provide strategies for incorporating good posture into everyday activities and promote postural awareness.
- ERGONOMIC ASSESSMENTS: Physiotherapists can assess an individual’s workstation or daily activities to identify ergonomic factors contributing to poor posture. They provide recommendations for optimizing workstations, adjusting chair and desk heights, using supportive equipment, and implementing proper body mechanics during activities. By making ergonomic modifications, individuals can maintain better posture and reduce the risk of postural strain.
- BREATHING AND DIAPHRAGMATIC TRAINING: Physiotherapists recognize the importance of proper breathing mechanics in maintaining good posture and alignment. They may teach individuals diaphragmatic breathing techniques and provide exercises to improve respiratory function. Proper breathing helps engage the core muscles, maintain spinal stability, and reduce muscle tension associated with poor posture.
- EDUCATION AND LIFESTYLE MODIFICATIONS: Physiotherapists play a vital role in educating individuals about the impact of poor posture and alignment on their health. They provide guidance on lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, taking regular breaks, incorporating movement into daily routines, and maintaining an active lifestyle. Physiotherapists empower individuals to take responsibility for their posture and make positive changes in their daily habits.
- PAIN MANAGEMENT: If an individual is experiencing pain related to poor posture and alignment, physiotherapists can provide pain management techniques. This may include modalities such as heat or cold therapy, electrical stimulation, or ultrasound to reduce pain and inflammation. By addressing pain, physiotherapists can help individuals engage more effectively in postural correction exercises and other interventions.
- LONG-TERM MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION: Physiotherapists not only address current postural issues but also focus on long-term management and prevention. They provide individuals with strategies and exercises to maintain good posture and alignment independently. They emphasize the importance of incorporating regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced muscle strength, and practicing proper posture in everyday activities. By promoting long-term habits and self-management, physiotherapists empower individuals to maintain optimal posture and alignment throughout their lives.
Physiotherapists are skilled professionals who can help individuals improve their posture and alignment through comprehensive assessments, manual therapy techniques, exercise prescription, postural retraining, ergonomic assessments, and education. Their expertise in musculoskeletal health allows them to address underlying issues, correct imbalances, and provide individuals with the tools and knowledge to maintain proper posture independently. Physiotherapy plays a vital role in improving posture, reducing pain, and enhancing overall musculoskeletal health, ultimately leading to better overall well-being.
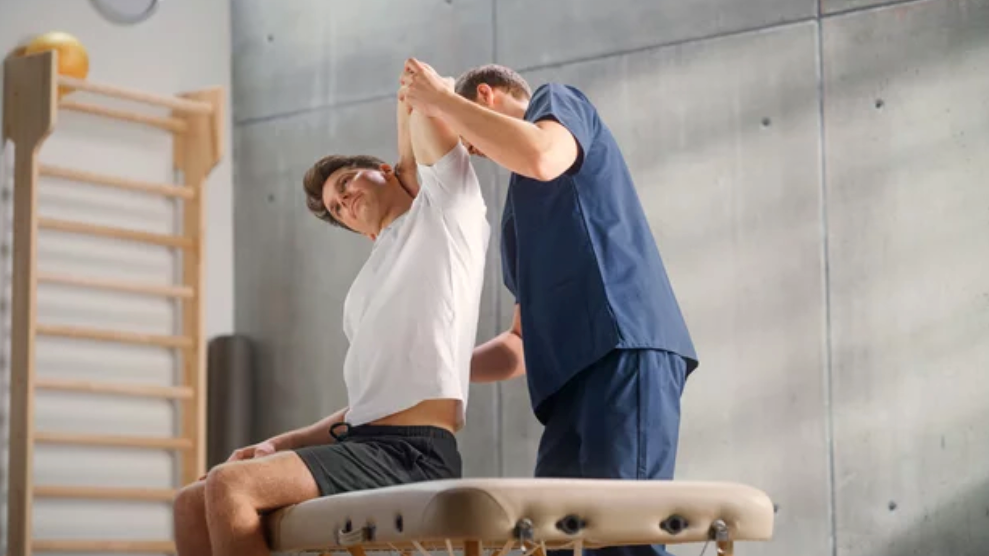

SPECIFIC PHYSIOTHERAPY TECHNIQUES FOR IMPROVING POSTURE AND ALIGNMENT:
Here are some specific physiotherapy techniques used for improving posture and alignment:
- PILATES: Pilates is a form of exercise that focuses on core stability, flexibility, and body awareness. It involves controlled movements and specific exercises that target deep postural muscles, including the abdominal, back, and pelvic floor muscles. Pilates can be highly effective in improving posture and alignment as it strengthens the core muscles that support the spine and promote proper alignment. Physiotherapists can incorporate Pilates exercises into their treatment plans, tailoring them to the individual’s specific postural imbalances. By practicing Pilates regularly, individuals can develop better postural control, improved muscle balance, and increased body awareness.
- POSTURAL TAPING: Postural taping involves the application of specialized tape to certain areas of the body to support proper alignment and encourage better posture. The tape is applied in specific patterns to provide sensory input, support weak or imbalanced muscles, and promote the desired postural position. Postural taping can be particularly beneficial for individuals who have difficulty maintaining good posture on their own or need additional support during activities that require proper alignment. Physiotherapists can assess the individual’s postural needs and apply the tape accordingly, providing support and feedback to facilitate better posture and alignment.
- ERGONOMIC ASSESSMENTS: Physiotherapists are skilled in performing ergonomic assessments to identify factors in a person’s work or home environment that may be contributing to poor posture. During an ergonomic assessment, the physiotherapist evaluates the individual’s workstation, seating, equipment, and overall work environment to identify any ergonomic risk factors. They may make adjustments to chair height, desk setup, monitor position, keyboard and mouse placement, and other ergonomic factors to promote better alignment and reduce postural strain. By optimizing the individual’s work environment, physiotherapists help individuals maintain proper posture and alignment throughout their daily activities, preventing postural-related issues.
- MANUAL THERAPY: Physiotherapists may use manual therapy techniques to address postural imbalances and promote proper alignment. These techniques include joint mobilizations, soft tissue massage, myofascial release, and stretching. Manual therapy can help release tight muscles, improve joint mobility, and correct imbalances in the musculoskeletal system. By addressing restrictions and imbalances, physiotherapists can help individuals achieve better alignment and posture. They may also use manual techniques to address any pain or discomfort associated with poor posture, promoting better alignment and reducing symptoms.
- SPECIFIC STRENGTHENING EXERCISES: Physiotherapists prescribe specific strengthening exercises to target weak muscles and promote balanced muscle development. These exercises are tailored to the individual’s specific postural imbalances and focus on strengthening the muscles necessary for maintaining proper alignment. For example, if an individual has rounded shoulders and forward head posture, exercises to strengthen the upper back, neck extensors, and deep neck flexors may be prescribed. By addressing muscle imbalances, strengthening weak muscles, and improving overall muscle tone, individuals can achieve better postural control and alignment.
- STRETCHING AND MOBILITY EXERCISES: Physiotherapists may also include stretching and mobility exercises in their treatment plans to address tight muscles and improve joint mobility. Tight muscles can contribute to poor posture and alignment by pulling the body out of its optimal position. Stretching exercises can help lengthen these muscles, allowing for better alignment and improved posture. Additionally, improving joint mobility can help restore proper movement patterns and reduce postural restrictions.
- BODY AWARENESS AND POSTURAL EDUCATION: Physiotherapists play a crucial role in educating individuals about proper posture and body mechanics. They provide guidance on maintaining good posture during different activities, such as sitting, standing, walking, and lifting. Physiotherapists teach individuals how to develop body awareness, recognize and correct postural imbalances, and make adjustments to maintain optimal alignment. By educating individuals about postural principles and providing practical strategies, physiotherapists empower individuals to take an active role in improving their posture and alignment.
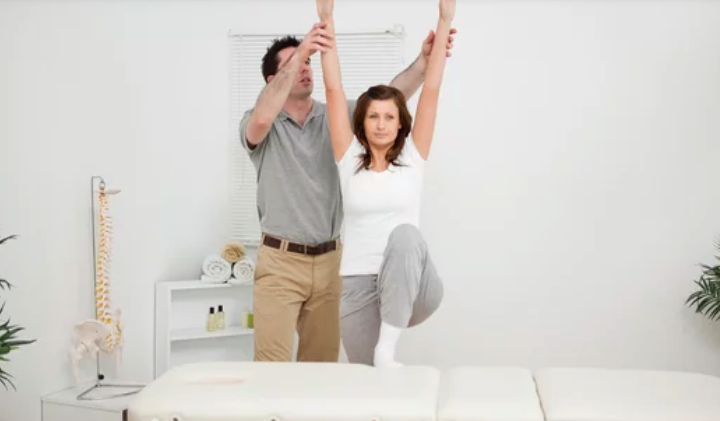

These specific physiotherapy techniques are effective in improving posture and alignment by addressing underlying imbalances, providing support, promoting proper muscle activation, and facilitating postural control. By incorporating these techniques into treatment plans, physiotherapists can help individuals achieve and maintain optimal posture and alignment, leading to improved musculoskeletal health and overall well-being.
HERE ARE SOME SELF-HELP STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE POSTURE AND ALIGNMENT:
- PRACTICE BODY AWARENESS: Pay attention to your body position throughout the day. Be mindful of slouching or hunching over and make a conscious effort to correct your posture.
- ERGONOMICS: Ensure that your workspace, whether at home or the office, is set up ergonomically. Use an adjustable chair and desk that support good posture. Position your computer monitor at eye level and maintain proper alignment of the keyboard, mouse, and other workstation tools.
- STRENGTHEN CORE AND BACK MUSCLES: Engaging in regular exercise, particularly exercises that target the core and back muscles, can help improve posture and alignment. Strengthening these muscles provides support for the spine and promotes better posture.
- STRETCHING AND FLEXIBILITY EXERCISES: Incorporate regular stretching and flexibility exercises into your routine to improve muscle flexibility and joint mobility. Focus on stretching the chest, neck, back, and hip muscles, as these areas are commonly affected by poor posture.
- POSTURAL EXERCISES: Consider incorporating specific postural exercises into your workout routine. These exercises can help strengthen the muscles that support good posture, such as the back extensors, core muscles, and postural muscles of the neck and shoulders.
- MINDFUL SITTING AND STANDING: Whether sitting or standing, be conscious of your posture. When sitting, keep your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and feet flat on the floor. When standing, distribute your weight evenly on both feet, engage your core muscles, and avoid slouching or hyperextending your back.
- USE SUPPORTIVE FURNITURE AND EQUIPMENT: Choose supportive furniture, such as chairs with lumbar support, and use ergonomic tools that promote good posture, such as supportive pillows and cushions.
- REGULAR BREAKS AND MOVEMENT: Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing in one position. Take regular breaks to stand up, stretch, and move around. Incorporate movement and exercise throughout the day to promote blood flow and reduce muscle fatigue.
- SEEK PROFESSIONAL HELP: If you are experiencing chronic pain or difficulty maintaining good posture, consider seeking help from healthcare professionals such as physical therapists or chiropractors. They can assess your posture, provide personalized recommendations, and guide you through exercises and techniques to improve alignment.
Poor posture and alignment can have significant effects on our health. It is crucial to be mindful of our posture, make necessary lifestyle adjustments, and engage in exercises and habits that promote good posture. By maintaining proper alignment, we can reduce the risk of musculoskeletal pain, headaches, digestive issues, breathing problems, and other associated health problems. Developing and maintaining good posture is an ongoing process that requires awareness, practice, and consistent effort, but the benefits to our overall health and well-being are well worth it.
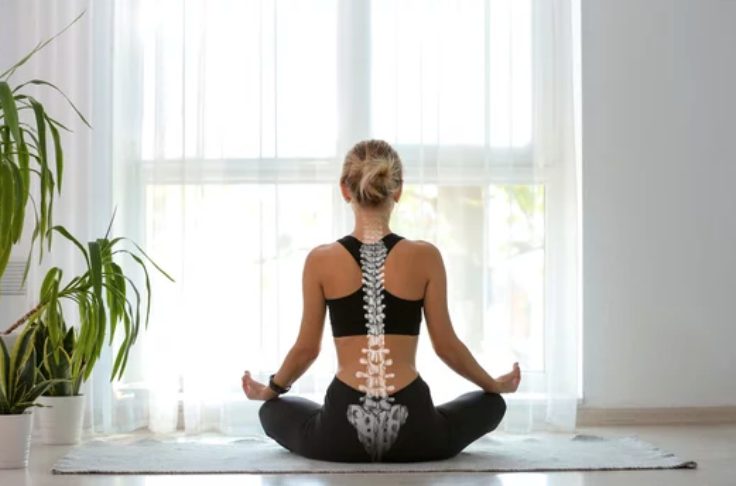






Good